广度优先搜索和深度优先搜索
广度优先搜索
自我理解:在搜索过程中是一层一层的搜索,搜索结束后才进入下一层。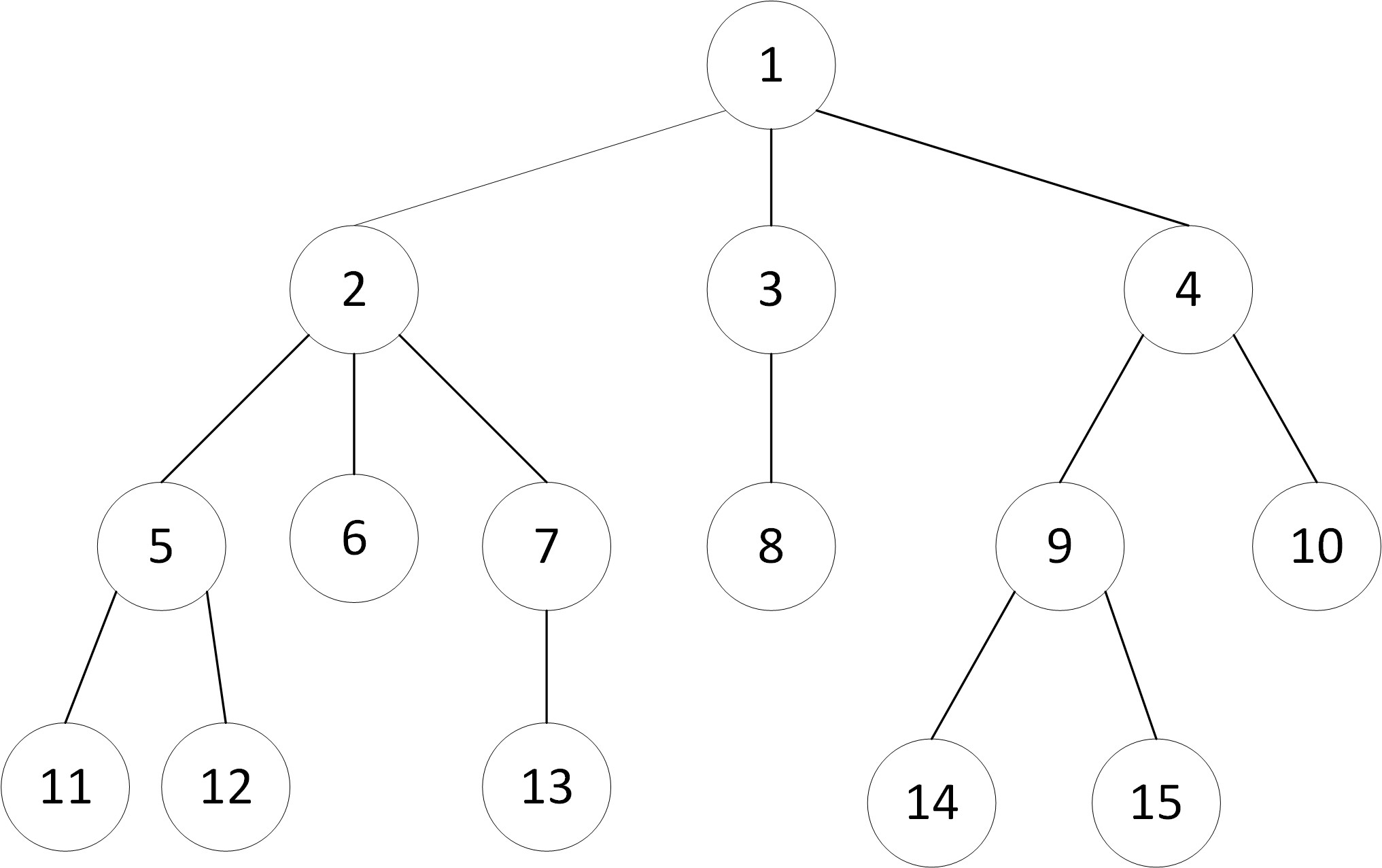
深度优先搜索
自我理解:搜索过程中优先探索各层第一个,之后逐层向下,直至到达底层,在返回上一层继续向下搜索,每搜索完则返回上一层。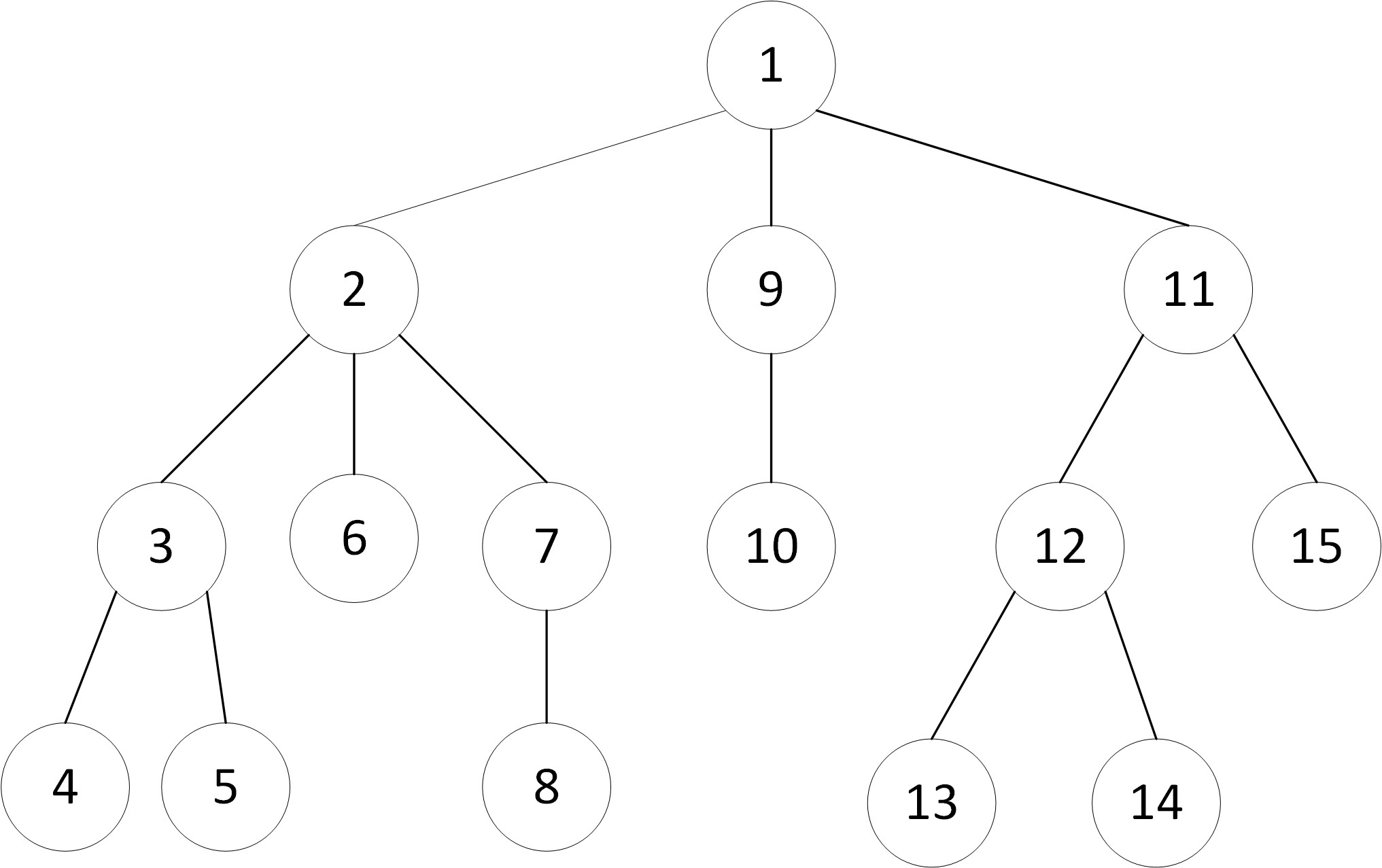
733. 图像渲染
有一幅以二维整数数组表示的图画,每一个整数表示该图画的像素值大小,数值在 0 到 65535 之间。
给你一个坐标 (sr, sc) 表示图像渲染开始的像素值(行 ,列)和一个新的颜色值 newColor,让你重新上色这幅图像。
为了完成上色工作,从初始坐标开始,记录初始坐标的上下左右四个方向上像素值与初始坐标相同的相连像素点,接着再记录这四个方向上符合条件的像素点与他们对应四个方向上像素值与初始坐标相同的相连像素点,……,重复该过程。将所有有记录的像素点的颜色值改为新的颜色值。最后返回经过上色渲染后的图像。
题目:我感觉题目是机翻的,下面我用我的理解说下题目。
有个m*n的矩阵,每个点都代表一个像素点。现在我们给定一个初始坐标点 (sr, sc) ,目的是将初始坐标点的颜色改为新的颜色值 newColor,并读取初始坐标点上下左右的四个坐标点,若有坐标点的颜色和初始坐标点颜色相同,则改为新颜色,同时以此点为中心寻找上下左右四个坐标点,并类推,直到结束。最后返回经过上色渲染后的图像。
具体题目链接
Python
class Solution:
def floodFill(self, image: List[List[int]], sr: int, sc: int, newColor: int) -> List[List[int]]:
xy=[(-1,0),(0,-1),(0,1),(1,0)]
oldColor,image[sr][sc]=image[sr][sc],newColor
m=len(image)
n=len(image[0])
if oldColor==newColor:
return image
que=[(sr,sc)]
index=0
while index<len(que):
ir,ic=que[index]
for x,y in xy:
if 0<=ir+x<m and 0<=ic+y<n and image[ir+x][ic+y]==oldColor:
que.append((ir+x,ic+y))
image[ir+x][ic+y]=newColor
index+=1
return image思路:广度优先搜索,xy是初始化上下左右坐标的增量,oldColor记录初始坐标的颜色。m,n代表矩阵的行数和列数。que代表队列(此处代码的队列不是真正的队列,仅是列表。)
首先将初始点增加到队列中,通过while循环队列,并搜索队列中点位的上下左右坐标,符合条件的则增加到队列中并修改颜色值,直至搜索完毕返回image
GO
func floodFill(image [][]int, sr int, sc int, newColor int) [][]int {
oldColor:=image[sr][sc]
x:=[]int{-1,0,0,1}
y:=[]int{0,1,-1,0}
if oldColor!=newColor{
depth(image,sr,sc,newColor,oldColor,x,y)
}
return image
}
func depth(image [][]int, sr int, sc int, newColor int,oldColor int,x []int,y []int){
if image[sr][sc]==oldColor{
image[sr][sc]=newColor
for i:=0;i<4;i++{
mx,my:=sr+x[i],sc+y[i]
if 0<=mx && mx<len(image) &&0<=my&&my<len(image[0]){
depth(image,mx,my,newColor,oldColor,x,y)
}
}
}
}思路:深度优先搜索,通过迭代实现。oldColor记录初始坐标点的位置,x和y初始化上下左右坐标的增量。深度搜索,是一直向下迭代,直到不符合在向上返回值,然后逐步返回。
695. 岛屿的最大面积
给定一个包含了一些 0 和 1 的非空二维数组 grid 。
一个 岛屿 是由一些相邻的 1 (代表土地) 构成的组合,这里的「相邻」要求两个 1 必须在水平或者竖直方向上相邻。你可以假设 grid 的四个边缘都被 0(代表水)包围着。
找到给定的二维数组中最大的岛屿面积。(如果没有岛屿,则返回面积为 0 。)
具体题目链接
class Solution:
def maxAreaOfIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:#深度搜索加迭代
ans=0
for r in range(len(grid)):#循环行
for c in range(len(grid[r])):#循环列
ans=max(ans,self.deph(grid,r,c))
return ans
def deph(self,grid,r,c):
if 0<=r<len(grid) and 0<=c<len(grid[0]) and grid[r][c]==1:
grid[r][c]=0
ans=1
xy=[(r-1,c),(r,c+1),(r,c-1),(r+1,c)]
for r1,c1 in xy:
ans+=self.deph(grid,r1,c1)
return ans
return 0思路:深度优先搜索加迭代
class Solution:
def maxAreaOfIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:深度搜索加栈
cur=0
for r in range(len(grid)):#循环行
for c in range(len(grid[r])):#循环列
ans=0
stack=[(r,c)]
while stack:
r1,c1=stack.pop()
if 0<=r1<len(grid) and 0<=c1<len(grid[0]) and grid[r1][c1]==1:
ans+=1
grid[r1][c1]=0
xy=[(r1-1,c1),(r1,c1+1),(r1,c1-1),(r1+1,c1)]
for r2,c2 in xy:
stack.append((r2,c2))
cur=max(cur,ans)
return cur 思路:深度优先搜索,但不采用迭代方式,而是建立栈的形式。(后进先出)
def maxAreaOfIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:#广度加队列
cur=0
for r in range(len(grid)):#循环行
for c in range(len(grid[r])):#循环列
ans=0
stack=[(r,c)]
i=0
while i<len(stack):
r1,c1=stack[i]
if 0<=r1<len(grid) and 0<=c1<len(grid[0]) and grid[r1][c1]==1:
ans+=1
grid[r1][c1]=0
xy=[(r1-1,c1),(r1,c1+1),(r1,c1-1),(r1+1,c1)]
for r2,c2 in xy:
stack.append((r2,c2))
i+=1
cur=max(cur,ans)
return cur思路:广度优先搜索加队列
GO
func maxAreaOfIsland(grid [][]int) int {
cur:=0
for i,_:=range grid{
for j,_:=range grid[i]{
ans:=0
stack:=[][]int{{i,j}}
for len(stack)!=0 {
r1,c1:=stack[0][0],stack[0][1]
stack=stack[1:]
if 0<=r1&&r1<len(grid) && 0<=c1&&c1<len(grid[0]) && grid[r1][c1]==1{
ans++
grid[r1][c1]=0
xy:=[][]int{{r1-1,c1},{r1,c1+1},{r1,c1-1},{r1+1,c1}}
for _,x_y:=range xy{
stack=append(stack,x_y)
}
}
}
if ans>cur{
cur=ans
}
}
}
return cur
}思路:广度优先搜索加队列,通过切片实现去除队列首位,实现队列。
图像渲染那题确实像机翻,我当时看了半天题目没看明白,然后切换成英文看完就明白在说啥了
翻译很有问题,我当时看了英文和评论区才明白意思。